

 News
News Industry News
Industry NewsVolatile organic compounds refer to organic compounds with a boiling point or initial distillation point lower than or equal to 250°C at normal temperature and pressure, referred to as VOCs. The components include benzene series, organic chlorides, freons, organic ketones, amines, alcohols, ethers, esters, acids and hydrocarbon compounds.
VOCs are widely present in people's daily lives and in the production process of enterprises. Such as the volatilization of oil and gas at gas stations, the diffusion of decoration paint during drying, and the daily disinfection of materials such as alcohol and iodine tincture. In addition, the fumes produced by families and catering companies during the cooking process also contain a large amount of VOCs. The process exhaust gas discharged by petrochemical plants during the production process of enterprises, the volatilization and leakage during the mining and transportation of fossil energy, the volatilization of organic materials such as paints, coatings, solvents, preservatives, and the waste gas generated by the incomplete combustion of various organic fuels.
VOCs have a great impact on air quality. Depending on their composition, VOCs can have varying degrees of negative impact on human health. Even if the concentration of various VOCs in the air is not high, when several VOCs co-exist in indoor air, their combined effect cannot be ignored. Therefore, real-time monitoring of VOCs in the air and exhaust gases in various scenes is of great significance for maintaining air quality and ensuring human safety.
Product Overview
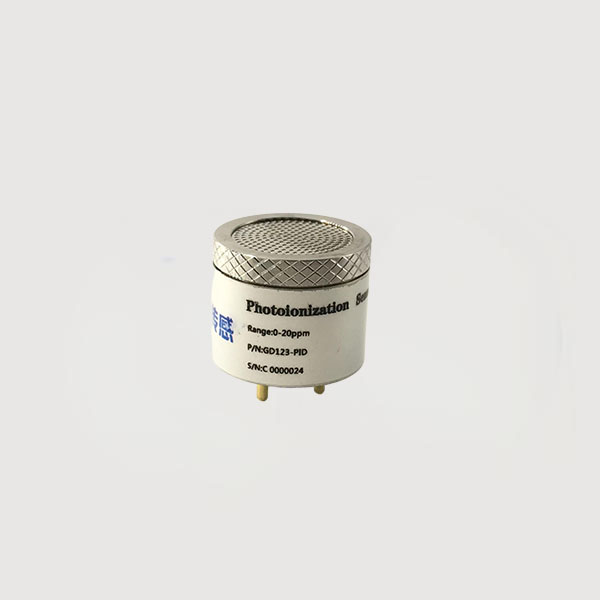

The high-performance photoionization PID sensor developed by Tensensor, GD-PID Photoion sensor, has the characteristics of high sensitivity, wide range and broad spectrum. It can detect thousands of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and some inorganic vapors in different application fields, and can provide a detection range of up to 10000ppm and a minimum detection limit of 1ppb, with extremely fast response speed and extremely high resolution. It is suitable for various types of handheld portable and field fixed instruments and meters, and can also be applied to various types of analytical instruments.
How do PID sensors sense VOCs?
Photoionization PID sensors use high voltage alternating electric fields to ionize certain inert gases to produce ultraviolet light. The energy of ultraviolet light is higher than that of visible light. It ionizes the gas into positively charged ions and negatively charged ions, and then uses electronic methods to detect the number of these ions to determine the concentration of the measured gas.
PID can detect compounds at concentration levels of one part per billion (ppb) to one part per million (ppm). It is a supplement to non-dispersive infrared, electrochemical, and catalytic combustion gas sensors, and is also a gas detector with relatively high technical content.
Advantages of PID sensor
High precision
High-precision photoionization sensors can detect organic gases at the ppb level, with an accuracy that exceeds that of most common sensors such as infrared sensors.
Non-destructive to the detected gas
Photoionization sensors ionize the gas after inhaling it, and the ions formed by the gas molecules re-form the original gas molecules after discharge, which is non-destructive to the original gas molecules.
Fast response speed
Except for the period of warming up after the gas detection system is turned on, in normal working conditions, the photoionization gas sensor can respond almost in real time and can be tested continuously. When detecting dangerous gases, it is of great significance to protect the health of the detection personnel.
For more information about PID solutions, please contact us for more detailed information:
ShanXi TengXing Sensor Technology Co.,Ltd
Web: www.tensensor.com
Email: [email protected]
Tel/WhatsApp: 86 18335818384