

 News
News Industry News
Industry NewsCarbon monoxide poisoning and first aid knowledge
Gas poisoning is a common method of poisoning in industry and daily life. Casualties and losses caused by gas poisoning occur every winter. While using gas, we must also understand some knowledge related to gas poisoning and first aid.
1. What is gas poisoning?
The toxicity of gas mainly comes from carbon monoxide. When a person is in an environment containing 0.1% (volume) carbon monoxide for about an hour, he will have headaches, nausea, vomiting, limb weakness and other poisoning phenomena. When the carbon monoxide content in the air reaches 1% (volume), the human body loses consciousness after inhaling it for 2-3 minutes. This is what we call gas poisoning (coal gas poisoning) in daily life.
2. What are the symptoms of gas poisoning?
Carbon monoxide poisoning is generally divided into acute and chronic poisoning.
2.1 Acute poisoning: Acute poisoning is divided into three types: mild, moderate and severe.
① Mild: manifested as dizziness, blurred vision, headache, tinnitus, nausea, vomiting, palpitations, and limb weakness. You should leave the scene, breathe fresh air or receive appropriate treatment, and the symptoms will disappear quickly.
② Moderate: In addition to the above symptoms, it also manifests as sweating, irritability, unsteady gait, pale skin or mucous membranes, blurred consciousness and even coma. If rescued in time, you can wake up quickly.
③ Severe: In addition to some or all of the moderate poisoning symptoms, the patient enters a coma. It can last for several hours or days. There are often clenched teeth, whole body twitching, incontinence, increased blood pressure, arrhythmia, etc. Severe poisoning is rescued in time and the symptoms gradually improve after escaping from coma. Some critically ill patients will show a series of severe damage to the nervous system after a period of "awake period" after waking up.
2.2 Chronic poisoning: Long-term exposure to carbon monoxide may have the following symptoms:
① Nervous system: headache, dizziness, insomnia, weakness, memory loss, lack of concentration, unstable blood pressure, and even tremors and unstable gait.
② Cardiovascular system: myocardial damage and insufficient blood supply to the coronary arteries, electrocardiogram changes, such as various types of arrhythmias, hypotension and atrioventricular block, etc.
3. Why does poisoning occur when burning gas indoors?
Gas combustion requires oxygen in the air to assist combustion. If the ventilation conditions are not good, the lack of oxygen will lead to incomplete combustion, and a certain amount of carbon monoxide will be produced. The concentration will gradually increase, aggravating the lack of oxygen in the human body until it finally suffocates.
4. What anti-poisoning measures should be taken?
4.1 Pay attention to checking whether there are loose leaks in the gas pipelines, valves and hose joints. If found, they should be repaired or replaced in time.
4.2 When the gas stove is out of use, check whether the valve is closed. It often happens that the burning stove goes out for other reasons. There are countless examples of accidents caused by mistaking the valve for closing and discharging gas for a long time, even poisoning and explosion accidents.
4.3 When using gas, keep good ventilation conditions in the kitchen.
5. What factors determine the severity of gas poisoning?
The severity of gas poisoning depends on the concentration and duration of exposure to gas. The higher the concentration and the longer the exposure time, the more severe the poisoning. Under the same concentration of gas, a worker is more seriously poisoned than a quiet person. It is not difficult to imagine that infants and children generally have more active gas exchange and require more oxygen, and are more susceptible to poisoning than adults in the same environment. For an anemic patient, the condition often worsens and even leads to death.
6. Rescue methods?
6.1 Move the patient to fresh air as soon as possible, unbutton the coat, and keep breathing unobstructed.
6.2 Perform artificial respiration, the easiest is mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration.
6.3 Oxygen inhalation, the most commonly used method is nasal cannula oxygen inhalation.
6.4 Chest massage should be performed immediately.
6.5 Send to hospital for emergency treatment.
7.Recommended detector sensor types
| Detection range | Max range | Resolution ratio | Load resistance | Life | Picture | |
| MQ2-CO-Φ14x5 | 0~5000ppm | 10000ppm | 1ppm | (500/1K/2K)Ω | 10 years |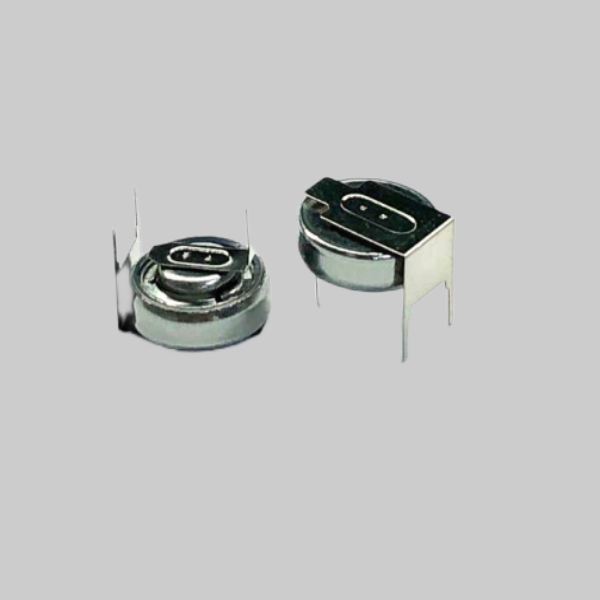  |
| MQ2-CO-φ14x14 | 0~1000ppm | 2000ppm | 1ppm | (500/1K/2K)Ω | 3 years |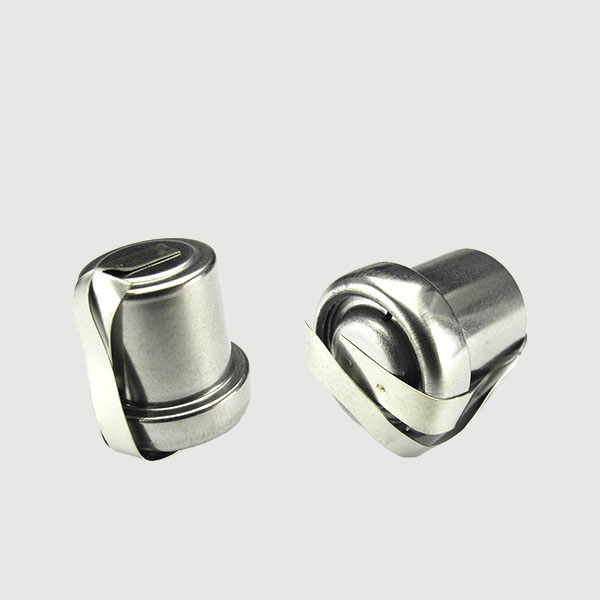  |
| MQ2-CO-Φ14×50 | 0~1000ppm | 2000ppm | 1ppm | 1000Ω | 5 years |