

 News
News Industry News
Industry NewsHazards of H2S Gas in Industrial Applications
Hydrogen sulfide(H2S) is a colorless, highly toxic, flammable, and explosive acidic gas. In industrial production, it is often considered a "silent killer," with its hazards manifesting primarily in the following three aspects:
1. Extreme Toxicity - Direct Threat to Life
This is the most lethal hazard of hydrogen sulfide. Its toxic mechanism involves inhibiting cellular respiration, binding to the ferric iron in cytochrome oxidases, blocking electron transport and cellular respiration, leading to tissue hypoxia, especially causing severe damage to oxygen-intensive organs such as the brain and heart.
High Concentration Lethality: At extremely high concentrations (e.g., above 1000 ppm), it can cause "electric shock-like" death, meaning that inhaling even a small amount will cause almost instantaneous collapse and respiratory arrest.
Concentration-Dependent Hazards:
0.1-10 ppm: A distinct "rotten egg" odor can be detected (but long-term exposure to low concentrations can lead to olfactory fatigue).
10-50 ppm: Irritates the eyes, throat, and respiratory tract, causing headaches, dizziness, and nausea.
50-200 ppm: Severely irritates the respiratory tract, causing coughing, conjunctivitis, and olfactory nerve paralysis (loss of smell, loss of warning signals!).
200-500 ppm: Causes pulmonary edema, bronchitis, and chemical pneumonia, seriously threatening life.
500-1000 ppm: Rapidly causes loss of consciousness, respiratory paralysis, and death within minutes.
2. Flammability and Explosiveness - Threats to Facilities and the Environment
Hydrogen sulfide is a flammable gas that can form an explosive mixture with air. It can ignite and explode upon contact with open flames or high heat.
Explosive Limits: The lower explosive limit in air is 4.3% (volume fraction), and the upper explosive limit is 46%.
Industrial Risks: In processes such as oil refining, natural gas processing, and chemical synthesis, if a leak occurs and reaches the explosive limit, a single spark could trigger a catastrophic fire or explosion, causing enormous casualties and property damage.
3. Corrosivity - Long-term damage to equipment and products
Hydrogen sulfide dissolves in water to form a weak acid (hydrosulfuric acid), which corrodes metal pipes, tanks, valves, and precision instruments.
Electrochemical corrosion: Leads to thinning of equipment walls, pitting corrosion, and the risk of leaks.
Hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC) and sulfide stress corrosion cracking (SSCC): Under high pressure, these pose a serious threat to high-strength steel equipment and may lead to sudden equipment failure.
The Importance of H2S Sensors
Under the aforementioned severe threats, hydrogen sulfide sensors have become indispensable "electronic sentinels" in industrial safety systems. Their importance is reflected in the following aspects:
Guardians of Life: It is the last and most critical technical line of defense protecting the lives of on-site workers. It can detect danger earlier than human sense of smell and issue an alarm before the dangerous concentration reaches harmful levels, buying valuable time for personnel evacuation and emergency response.
Early Warning System for Accidents: Through real-time, continuous monitoring, the sensor can issue an alarm in the early stages of a leak, thus preventing small leaks from escalating into catastrophic accidents (such as large-scale poisoning, fires, and explosions).
The "Eyes" of Industrial Processes: Many processes (such as natural gas purification, sulfur recovery, and papermaking) require precise control of hydrogen sulfide concentrations. The sensor provides crucial data for process control, ensuring product quality and process stability.
The Cornerstone of Compliance: Countries worldwide (such as China's "Occupational Disease Prevention and Control Law" and "Occupational Exposure Limits for Hazardous Factors in the Workplace") have strict legal regulations regarding the permissible concentration of hydrogen sulfide in workplace air. Installing and using hydrogen sulfide sensors is a necessary measure for enterprises to fulfill their legal responsibilities, protect the occupational health of their employees, and avoid legal disputes.
Product Recommendation
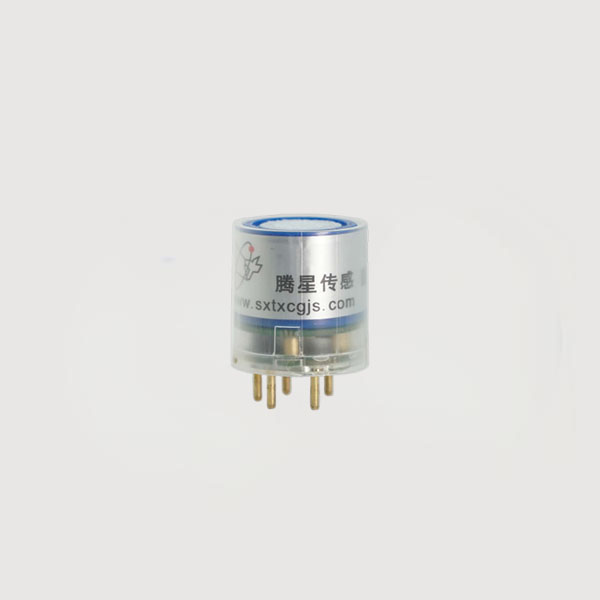

TE03-H2S electrochemical H2S module
In the industrial, H2S is a hazardous chemical that poses a triple threat: extreme toxicity, explosiveness, and corrosiveness. Relying on human senses to mitigate its risks is highly unreliable and extremely dangerous. Hydrogen sulfide sensors, as a reliable technological means, bear the core mission of real-time monitoring, early warning, protecting lives, preventing accidents, and ensuring production. Therefore, in industrial environments where hydrogen sulfide may be present, the widespread and correct use of H2S sensor module is not an option, but a mandatory safety responsibility and a fundamental requirement.