

 News
News Industry News
Industry NewsHazards of HCL Gas in Industrial Environments
Hydrogen chloride is a colorless gas at room temperature. It reacts with water vapor in the air to form a white acid mist with a strong, pungent odor. It is widely used in various industries, including chemical, metallurgical, electroplating, pesticide, and semiconductor manufacturing.
1. Direct Hazards to Human Health
Strong Irritation and Corrosiveness: HCl gas has extremely strong irritant and corrosive effects on the eyes, skin, and respiratory mucous membranes. Short-term exposure to low concentrations can cause symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, sore throat, and chest tightness.
Acute Poisoning: Exposure to high concentrations can lead to chemical bronchitis, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and in severe cases, even death due to respiratory failure.
Long-Term Chronic Effects: Long-term exposure to low concentrations of HCl can cause chronic rhinitis, bronchitis, dental erosion, and gastrointestinal dysfunction.
Indirect Hazards: HCl acid mist can adhere to equipment surfaces, creating a corrosive environment that may lead to equipment malfunctions, secondary accidents, and indirectly endanger personnel safety.
2. Severe Corrosion of Production Equipment and Facilities
HCl, especially the hydrochloric acid it forms, is extremely corrosive to most metallic materials (such as steel, copper, and aluminum).
It corrodes pipes, reactors, storage tanks, electrical equipment, control circuits, and building structures, leading to:
Equipment damage and shortened lifespan: Increased maintenance costs and equipment replacement frequency.
Increased leakage risk: Corroded pipes or containers are more prone to rupture, causing larger-scale leaks.
Production interruption: Production line shutdowns due to equipment repair or replacement result in significant economic losses.
3. Environmental Pollution
Leaked HCl gas can diffuse into the surrounding environment, forming acid rain, polluting soil and water bodies, and harming plant and animal growth.
It disrupts the ecological balance, and companies may face severe legal and regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
4. Catalyst with Flammable and Explosive Risks
Although HCl itself is neither flammable nor explosive, it can react with some reactive metals (such as aluminum and zinc) to release hydrogen gas. Hydrogen is a highly flammable and explosive gas, which can indirectly cause fires or explosions.
Product Recommendation
The HCL leak can not only endanger employee health and disrupt production, but also potentially cause a major safety accident. Therefore, building a reliable and sensitive gas monitoring barrier is of paramount importance in industrial safety management. The core of this barrier lies in selecting a suitable HCL gas sensor.
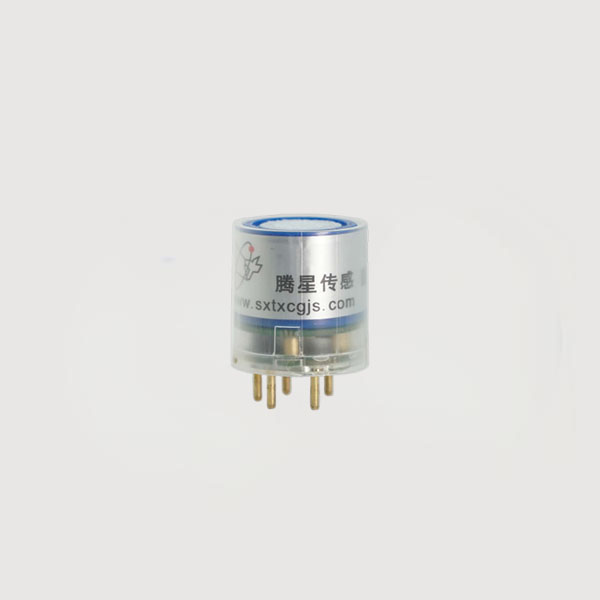

TE03-HCL electrochemical HCL module
Tensensor's TE03-HCL product features high sensitivity(resolution is 0.1 ppm), low power consumption, cost-effectiveness, and fast response speed, and can provide UART output, making it ideal for gas detection in personal protective equipment and general industrial environments.