

 News
News Industry News
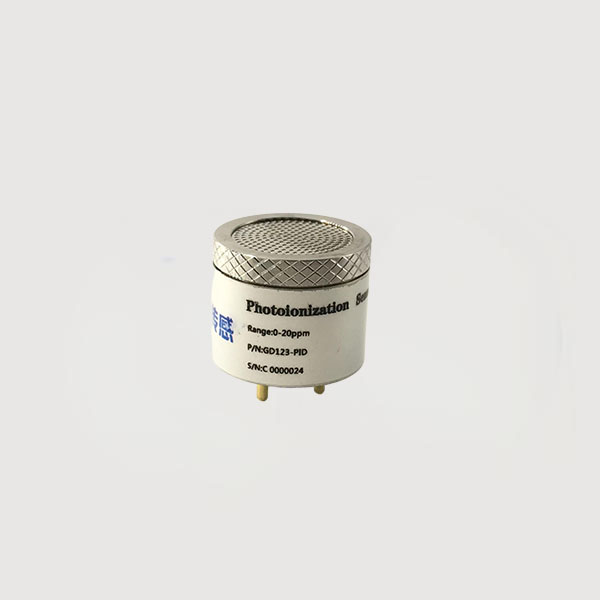
Industry NewsPhotoionization PID sensors use an ultraviolet (UV) lamp to ionize organic molecules into detectable positive and negative ions (ionization). The concentration of the gas being measured is then determined electronically by detecting the amount of these ions.
PID sensors can detect extremely low concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other toxic gases. Their high sensitivity to VOCs makes them irreplaceable in emergency accident detection.

1. UV Lamp Energy
Theoretically, all chemical substances can be ionized, but the energy required for them to ionize varies. This energy required to ionize a compound is called the "ionization potential" (IP), measured in electron volts (eV). The energy emitted by a UV lamp is also measured in eV. If the ionization potential (IP) of the gas being measured is lower than the lamp's output energy, the gas can be ionized and thus detected.
When selecting a PID sensor, the output energy of the UV lamp is typically a key consideration to infer the types of gases the sensor can ionize. Common products typically offer three options: 9.8 eV, 10.6 eV, and 11.7 eV.
2.Detection Range
After determining the type of gas to be detected, it is also necessary to determine the concentration of the gas being measured, which involves the gas concentration detection range of the PID sensor, which is generally a wide range from a few ppb to tens of thousands of ppm.
3.Resolution and Sensitivity
Resolution is the smallest change in a measurand that a sensor can detect within a specified measurement range. PID sensors have extremely high sensitivity, reaching the ppb level, and offer outstanding advantages in response speed and sensitivity.
4.Linearity
PID sensors exhibit good linearity, displaying linear changes over most of their measurement range.
5.Response time T90
When the sensor encounters a reactive gas, it converts the photoelectric signal into an electrical signal. T90 refers to the time required for the sensor to rise from a reading of 0 to 90% of the concentration of the gas measured in the environment.
6.The Influence of Ambient Temperature and Humidity
Sensors are affected by temperature and humidity, causing output values to drift and impacting product use. Therefore, assessing the impact of temperature and humidity on sensors is crucial. The GD-PID sensor is less affected by environmental interference, with an error not exceeding 10%.
The GD-PID is a high-performance photoionization PID sensor characterized by high sensitivity, wide range, and broad spectrum. It is fully customizable and can seamlessly replace imported brand products. It can detect thousands of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and some inorganic vapors in various applications. It can be used in various handheld portable and field-mounted instruments, as well as various types of analytical instruments, making VOCs monitoring more efficient!